What is a SIEM platform?
A security information and event management (SIEM, pronounced “sim”) platform is a cybersecurity solution for organizations to detect, analyze, and mitigate security threats before those threats disrupt operations. A SIEM platform collects logs, network data, and additional information from applications, servers, users, and devices. The key features of SIEM include log management, event correlation, and incident monitoring through a centralized tool that provides alerting, tracing, and reporting. A SIEM platform is a crucial tool for managing an organization’s security posture and for compliance management.
What is a cloud-based SIEM platform?
A cloud-based SIEM platform operates as a software as a service (SaaS) solution to provide the capabilities of a SIEM for an organization. A cloud-based SIEM platform has several advantages over a platform that must be hosted and maintained on an organization’s premises. These advantages include continuous application updates; the ability to easily scale supporting infrastructure as needed; and comprehensive automation, alerting, and analysis tools.
What are the biggest security challenges facing cloud-native organizations?
When it comes to managing security, the key challenges and issues affecting organizations right now are the following:
The scattering of security data originating from multiple or fragmented sources across an organization makes it a challenge for security professionals to review historical security data or to obtain a comprehensive view of the organization’s current security posture.
Without centralized monitoring, detecting and responding to threats may be slow and inefficient, which could increase an organization’s level of risk.
Limited visibility into network activities makes it difficult to identify suspicious behavior or security breaches.
A lack of automated tools reduces a security team’s ability to identify and correlate threats across a wide range of different systems.
A lack of a comprehensive security monitoring platform reduces a security team’s ability to identify and correlate threats across a wide range of different systems.
Without comprehensive, detailed logs and context centralized in one tool, incident management becomes an inefficient, fragmented, and often manual process.
What are the key benefits of a cloud-based SIEM platform?
A cloud-based SIEM platform offers consolidated, centralized security monitoring for an organization, enabling security teams to react to alerts and protect infrastructure and critical resources. A SIEM platform accomplishes this and more through:
Enhanced, automated threat detection. A cloud-based SIEM platform uses advanced analytics, correlation rules, and behavioral analysis to identify subtle threats that could be missed by professionals relying on separate security tools.
Centralized monitoring. By consolidating security data and event monitoring into a single, centralized platform, a SIEM solution presents a comprehensive view of an organization’s security status. This consolidation not only improves awareness, but it also reduces response times for security incidents.
Forensic capabilities. A SIEM platform facilitates security investigations by providing access to historical security data, consolidated in one location. This critical historical context helps with root cause analysis, identifies the scope and breadth of potential threats, and provides teams with clear timelines of previous security-related events.
Alert management. A SIEM platform can consolidate and manage high volumes of security alerts. Rules-based prioritization filters out merely informational alerts and surfaces those indicating higher urgency, helping reduce alert fatigue and enabling teams to focus on critical threats.
Scalability and flexibility. A modern SIEM solution should accommodate growing data volumes and evolving security needs. A SIEM platform should also flexibly integrate with both external third-party and custom tools to provide a full view into the security posture of any organization’s environment.
How does a cloud-based SIEM platform work?
A cloud-based SIEM system collects, aggregates, correlates, and analyzes security data from sources within an organization’s IT infrastructure. Here’s a breakdown of how a modern SIEM platform works:
Ingestion of security log and event data into a centralized repository: Instead of using separate tools for tracking, analysis, and reporting, a SIEM platform ingests, integrates, and normalizes high volumes of security-related data from disparate sources into a central repository.
Long-term storage: A SIEM platform uses its centralized repository to retain data for real-time and historical querying, forensic analysis, and compliance and auditing.
Real-time and historical threat detection engine: A SIEM platform applies correlation rules to identify threat patterns collected in its repository for both real-time and historical data. Graphical interfaces present information through the SIEM platform to help security teams examine historical timelines, system-level events, network traffic, app access and usage, user account data—correlated with threat intelligence.
Investigative tools to understand user and entity behavior: A SIEM platform provides automation and tools to better understand user and entity behavior across the organization. Graphical dashboards can visualize user activity across timelines, add search/query capabilities, correlate events with users and infrastructure entities, and review data regarding system and user accounts, malicious IP addresses, domains, and so on.
Automation via security response and orchestration playbooks: Playbooks (either built into the platform or available as external integrations) are predefined response procedures that guide security teams through investigating and remediating any detected threats. Playbooks can connect to automated steps such as scripts to run, or they can recommend and facilitate manual responses like blocking an IP address, disabling a user, or removing access permission to an entity.
Cloud-based SIEM platform use cases
Besides standard threat detection and incident responses, other use cases for SIEM platforms include:
- Compliance management: Many industries must adhere to regulatory requirements that mandate security controls and reporting standards. A cloud-based SIEM platform helps organizations comply with these requirements by providing detailed audit trails and automated reporting capabilities.
For example, a healthcare organization using a cloud-based SIEM platform can generate compliance reports for HIPAA by tracking access to sensitive patient data and ensuring that only authorized personnel have access.
- User behavior analytics (UBA): A cloud-based SIEM solution can monitor user activities and identify deviations from normal behavior patterns to address insider threats, compromised accounts, and other suspicious activities.
For example, if a user suddenly starts downloading large volumes of sensitive data at unusual hours, a cloud-based SIEM platform can flag this activity as suspicious, prompting further investigation.
- Cloud infrastructure monitoring: Cloud-based SIEM platforms provide visibility into the security posture of cloud infrastructure, enabling organizations to monitor configurations, access controls, and resource usage.
For example, a cloud-based SIEM platform can detect changes in security group access that expose cloud resources to the public internet, allowing security teams to take corrective actions before an attacker exploits the vulnerability.
- Advanced persistent threat (APT) detection: Advanced persistent threats are stealthy and sophisticated attacks that occur over extended periods. A cloud-based SIEM platform can help detect these threats by correlating subtle indicators across various data sources.
For example, a cloud-based SIEM platform may identify a series of low-level alerts that, when correlated, suggest an APT is attempting to establish a foothold in the network by exploiting a vulnerability in a cloud application.
- Threat hunting: Threat hunting identifies hidden or advanced threats that might not trigger standard security alerts. By aggregating and correlating log data from various sources, security analysts can use advanced analytics to search for and identify unusual patterns and potential indicators of malicious activity.
For example, a security analyst in a financial institution might use a SIEM platform to identify unusual login patterns, such as repeated attempts from an unfamiliar location. By correlating this data with access logs, the analyst could discover unauthorized access to sensitive customer information, leading to immediate actions to secure the account and investigate the breach.
Industry shifts in approaching security
As technology and the nature of threats change, SIEM platforms must also evolve to meet these challenges. Several of these include:
Cloud integration: On-premises SIEM solutions are moving to cloud-based SIEM platforms, driven by industry-wide cloud infrastructure adoption and the need for scalable, flexible, and cost-effective security solutions.
Advanced analytics and machine learning: Advanced analytics and machine learning enhance threat detection, reduce false positives, and provide deeper insights into security events.
Increased focus on automation: Increased use of automation can integrate with security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) capabilities to streamline incident responses, reduce manual efforts, and improve operational efficiency.
Integration with other security tools: SIEM platforms are now more commonly integrated with a wider range of security tools—such as endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions, user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) systems, and threat intelligence platforms—to provide a more comprehensive security posture.
Improved user experience: Enhancing the user experience with more intuitive interfaces, customizable dashboards, and better reporting capabilities makes SIEM tools more accessible and useful for security teams.
Challenges to implementing a cloud-based SIEM platform
Security teams implementing a cloud-based SIEM solution face certain challenges, including the following:
Complexity of consolidation and integration
Challenge: SIEM systems must integrate with existing IT infrastructure components, such as servers, network devices, applications, and cloud services, to centralize security data. This integration should also extend to user accounts, account privileges, and access rights. Achieving this level of integration can be complex and time consuming for an organization, and it may involve multiple teams with differing responsibilities.
Solution: A thorough assessment of existing systems, a clear integration plan, and a thorough understanding of responsibilities across teams can help manage this complexity. In addition, deploying a SIEM solution with broad compatibility and APIs makes the integration of different security components much easier to achieve.
Data volume and storage
Challenge: SIEM platforms must collect, analyze, and store large volumes of log and event data, demanding larger storage capacities that could impact system performance.
Solution: Implementing data retention policies, compressing data, and using scalable cloud storage solutions can help effectively manage data volume and associated costs. Integration teams may favor cloud providers who do not restrict the amount of infrequently used data in cold storage and who rehydrate the data when it is needed. Rehydrating data refers to data that is retrieved from cold storage when needed.
Logging without Limits™ is a feature of Datadog Log Management that allows users to collect and manage large volumes of logs without having to choose which ones to keep. Some of the advantages of this feature include:
- Cost effectiveness: Logging without Limits™ allows users to collect all logs without having to choose which ones to leave behind.
- Cloud-scale volumes: Logging without Limits™ can handle terabytes of log data every day.
- Dynamic log selection: Users can dynamically decide which logs to index for further analysis.
- Archiving: Logging without Limits™ provides intuitive archiving for security and IT teams.
- Live tail: Logging without Limits™ allows users to observe everything happening in real time.
- Troubleshooting: Logging without Limits™ provides a streamlined troubleshooting experience in the Log Explorer.
- Security threats: Logging without Limits™ powers Datadog Cloud SIEM, which detects security threats without requiring users to index logs.
Tuning and noise reduction
Challenge: At the outset, a SIEM deployment processes vast amounts of log data and produces a high volume of alerts, including false positives. These messages can overwhelm teams and obscure genuine threats.
Solution: Regularly tuning detection rules, refining correlation algorithms, and using machine learning can improve alert accuracy and reduce false positives.
Resource and skill requirements
Challenge: A SIEM solution requires skilled personnel to effectively manage, maintain, and analyze data. Obtaining that talent can be challenging for organizations.
Solution: Investing in training for security analysts or partnering with managed security service providers (MSSPs) can address resource gaps.
Features to look for in a cloud-based SIEM platform
Some important features to look for when considering a SIEM platform include:
Real-time and historical security analytics: For real-time analysis, a detection engine should analyze directly on ingest and not after costly indexing. Detection rules and analytics are applied continuously to streaming data, allowing for immediate identification of threats and anomalies. For historical analysis, the detection engine should examine past data efficiently to surface embedded threats. Scheduled jobs can automatically process and analyze past data at regular intervals for systematic review of historical logs and events.
Cost-effective log ingestion and retention: Using automation pipelines for ingestion improves log management and observability. Log storage should be decoupled from indexing for cost effectiveness.
Advanced query language: An easy-to-use, intuitive query language aids in the retrieval, filtering, and analysis of log and event data, enabling searches for specific information and making it easy to identify patterns or anomalies.
SOAR: This is a set of tools and services designed to improve an organization’s security posture by automating and coordinating responses to cyberthreats. Security orchestration connects security tools and systems, internal and external, to consolidate processes. Automation is used for repetitive and time-consuming tasks and also for running playbooks to resolve specific incidents. Response enables faster and more accurate remediation efforts for security incidents.
UEBA: This is a cybersecurity solution that uses machine learning, statistical analysis, and behavioral analytics to detect unusual and potentially harmful activities within an organization’s network. It incorporates behavioral baselines, anomaly detection, and machine learning; integrates with other security tools; and focuses on insider threat detection.
Dashboards: The platform should have visual interfaces that aggregate, display, and organize security data and metrics, allowing security teams to quickly monitor, analyze, and respond to security events and trends across their environment.
Learn more
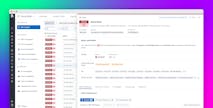
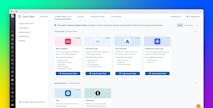
Built on Datadog’s advanced log management solution, Datadog Cloud SIEM offers an intuitive user experience that provides threat detection and investigation for dynamic, cloud-scale environments.
With Cloud SIEM, organizations can analyze security logs in real time, apply out-of-the-box integrations and rules to detect threats, and investigate those threats with expert guidance. Cloud SIEM allows teams to collaborate and report on security thanks to a shared view of security-related data within a single platform.