Neha Shah

David M. Lentz
Dell EMC Isilon is a petabyte-scale network attached storage (NAS) system that allows you to archive unstructured data. Isilon operates in a cluster to provide high availability, and you can scale up its throughput, IOPS, and storage space by adding nodes to your cluster. Isilon automatically replicates your data throughout the cluster to ensure durability and provides caching to minimize data retrieval latency.
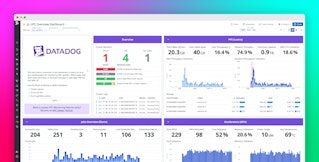
We’re pleased to announce that the Dell EMC Isilon integration from Crest Data Systems is now available in the Datadog Marketplace. Now you can track the health of all of your Isilon clusters on five out-of-the-box dashboards revolving around cluster, quota, file system, protocol, and node information, alongside telemetry from the rest of your stack. This integration also enables you to provide Isilon monitoring access to users without granting them access to your cluster.

In this post, we’ll show you how the Dell EMC Isilon integration from the Datadog Marketplace allows you to:
- Track the health of your Isilon clusters
- Monitor the performance of individual nodes
- See how Isilon’s performance affects your application
Keep your clusters healthy
Whether you use Isilon as the data layer in a distributed application or as an archive of infrequently accessed data, monitoring cluster performance can help you detect and troubleshoot bottlenecks. You can get started quickly using the out-of-the-box cluster dashboard, which shows you aggregated performance and resource usage across all of your clusters, or from a single cluster that you’ve specified using the dashboard’s template variables.
Isilon clusters replicate data across disk pools, which are logical collections of disks that act together as a single unit of storage. At a higher level, disk pools are organized into node pools, so monitoring node pool throughput and utilization gives you a quick view of one important dimension of your cluster’s health.

Other information on the cluster dashboard helps you understand your cluster’s CPU usage, throughput, and connection rate. And you can customize the dashboard to track related metrics from the rest of your infrastructure and other applications, making it easy to correlate metrics from throughout your stack for faster troubleshooting.
Ensure the health of your nodes
If your cluster-level monitoring indicates any issues with the overall health of your Isilon clusters, you can troubleshoot the problem by monitoring individual nodes. Isilon stores data across multiple nodes in the cluster, and each node plays a role in replicating, storing, and serving data. While your cluster can tolerate the failure of some nodes, it’s important to quickly identify an impaired node so you can replace it in time to maintain your cluster’s performance and availability. For example, to prevent nodes from overheating—which can cause them to perform poorly and even fail completely—you can create an alert to automatically notify you if any node’s CPU temperature rises above a threshold you identify.
The node dashboard helps you see resource usage and performance metrics—as well as the temperature and power usage of each node in your cluster. The screenshot below shows that the outbound file system throughput of node i-01230123 declined sharply at 16:55 while its CPU and memory usage metrics remained steady. This could indicate a problem with the node’s networking, such as a configuration issue or a failing network interface. To see the effect of this issue on the cluster, you can use the template variables at the top of the dashboard to see the sum of the throughput metrics from all of the nodes in the cluster.

See how Isilon’s performance affects your application
If your application frequently accesses and updates data in Isilon storage, the quality of your user experience depends on your cluster’s performance. You can easily troubleshoot performance issues, such as increased page load times, by correlating application metrics with Isilon metrics to help you determine whether latency in your cluster is a factor.
For example, you can use the file system dashboard to track Isilon’s cache performance, which influences how quickly your application can access archived data. Isilon uses multiple levels of caching to decrease latency throughout the cluster. A node’s level 1 (L1) cache holds data that the node has requested from other nodes in the cluster, and its L2 cache makes data available over the network to other nodes. Nodes that use SSD storage may also have an L3 cache, which contains data that has been evicted from L2.
Isilon populates its caches by prefetching data—predicting which data is likely to be accessed next and loading it into a cache before it’s requested. It does this based on the client’s data access pattern—specifically, by detecting whether the client is streaming data from within a single file or accessing a series of files in sequential order of their filenames.
In the screenshot below, the L2 Cache Prefetch Hit Rate dropped significantly on all nodes in the cluster. This could be due to a change in the application’s data access pattern, for example from streaming data (which Isilon can prefetch aggressively) to random file access (which does not allow for as much prefetching). Observing these cache performance metrics can be helpful for understanding changes in your app’s performance.

Start your Isilon monitoring in the Datadog Marketplace
Crest Data Systems’ integration for Dell EMC Isilon monitoring is now available for purchase in the Datadog Marketplace and includes a 14-day free trial. See our documentation for more information about monitoring Isilon in Datadog.
The ability to promote branded monitoring tools in the Datadog Marketplace is one of the benefits of membership in the Datadog Partner Network. If you’re interested in developing an integration or application for the Datadog Marketplace, contact us at marketplace@datadog.com.